CI/CD integration
Outerbounds integrates seamlessly to CI/CD systems. Read this comprehensive blog post about the topic.
GitOps for Outerbounds
The following diagram illustrates a typical CI/CD pattern:
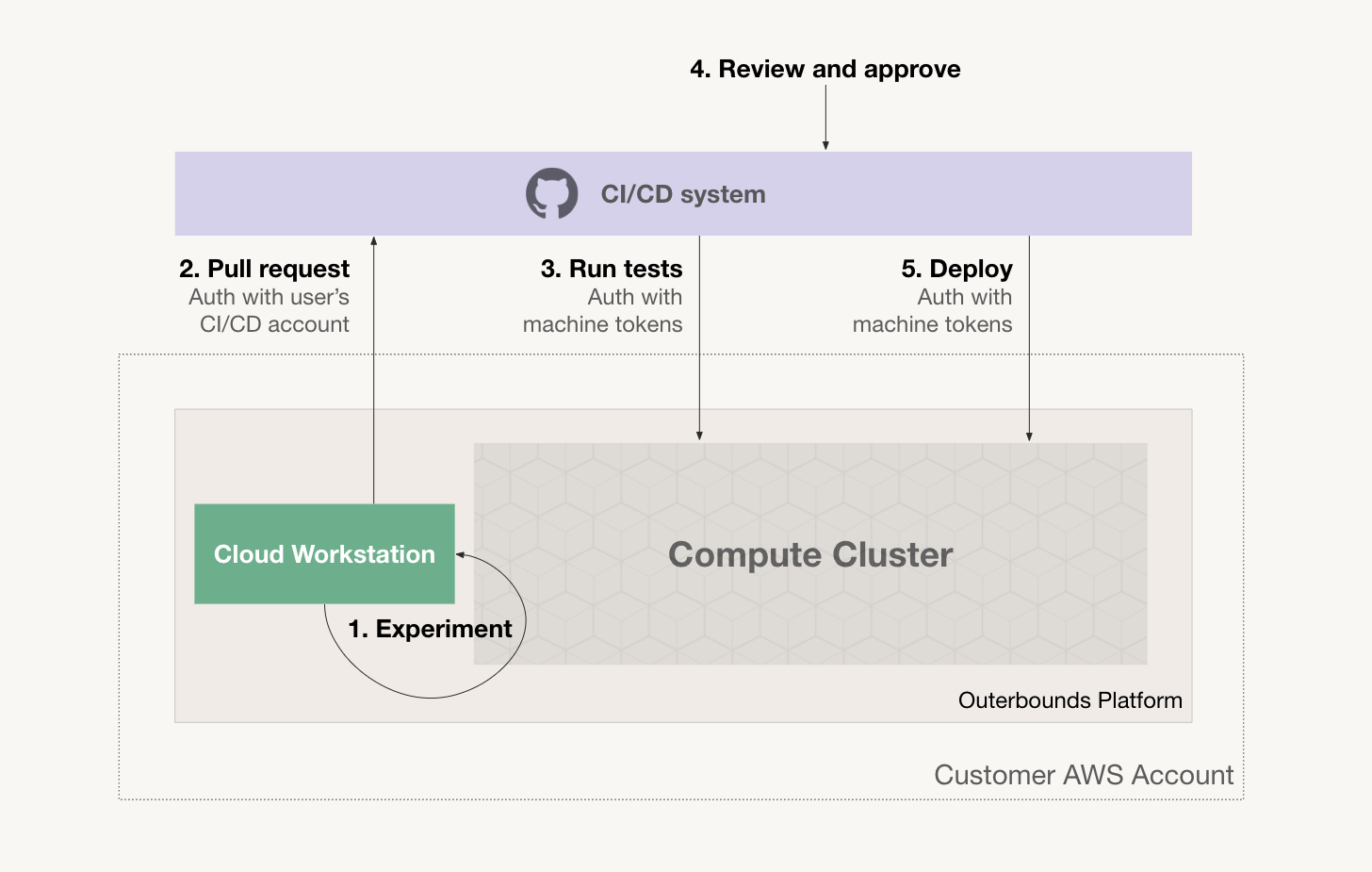
The user experiments and prototypes code on a cloud workstation or locally on a laptop. Crucially, the user is able to test their code at scale quickly and autonomously in to the Outerbounds cluster.
When the code seems to work adequately, they commit it and open a pull request. They authenticate with the CI/CD system using their personal credentials.
The CI/CD system, e.g. GitHub Actions, CircleCI can be configured to launch a test suite automatically when a pull request is opened. The CI/CD system submits workloads to Outerbounds authenticating as a machine user.
After tests pass, a human reviewer reviews the pull request. The reviewer may tag the pull request as approved and a corresponding Metaflow tag can be applied to tests as well, signalling a successful PR.
After the PR has been approved, the CI/CD system deploys the flow either as a new production version or as , running concurrently with the production version so its performance can be evaluated live.
Supported CI/CD Platforms
Outerbounds supports all major CI/CD platforms through OIDC-based authentication:
- GitHub Actions - Native OIDC support
- GitLab CI/CD - Native OIDC support via
id_tokens - Azure DevOps - Azure AD federation
- CircleCI - OIDC token support
Each platform uses a similar pattern:
- Configure a machine user in Outerbounds
- Set up OIDC authentication in your CI/CD config
- Use
obproject-deployto deploy your project
Using Outerbounds with GitHub Actions
This video and the accompaniying repository demonstrates the key workflows in practice:
Follow instructions in this repository to set up OBP work with GitHub Actions.
Example GitHub Actions workflow
name: Deploy Project
on:
push:
branches: [main]
pull_request:
branches: [main]
permissions:
id-token: write
contents: read
jobs:
deploy:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
with:
fetch-depth: 0
- name: Set up Python
uses: actions/setup-python@v5
with:
python-version: "3.12"
- name: Install dependencies
run: pip install outerbounds ob-project-utils pyyaml
- name: Configure Outerbounds
run: |
PROJECT_NAME=$(yq .project obproject.toml)
PLATFORM=$(yq .platform obproject.toml)
CICD_USER="${PROJECT_NAME//_/-}-cicd"
outerbounds service-principal-configure \
--name $CICD_USER \
--deployment-domain $PLATFORM \
--perimeter default \
--github-actions
- name: Deploy Project
run: obproject-deploy
Using Outerbounds with GitLab CI/CD
GitLab CI/CD supports OIDC authentication via the id_tokens keyword. See the GitLab CI template for a ready-to-use configuration.
The aud value in id_tokens must match your Outerbounds platform URL (e.g., https://my-company.outerbounds.com). This cannot be dynamically read from obproject.toml because GitLab evaluates id_tokens at pipeline creation time, before any scripts run. Update this value when setting up a new project.
Example .gitlab-ci.yml
stages:
- deploy
deploy:
stage: deploy
image: python:3.12
rules:
- if: $CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE == "merge_request_event"
- if: $CI_COMMIT_BRANCH == "main"
id_tokens:
OUTERBOUNDS_ID_TOKEN:
aud: https://my-company.outerbounds.com # Update to your platform URL
script:
- wget -qO /usr/local/bin/yq https://github.com/mikefarah/yq/releases/latest/download/yq_linux_amd64
- chmod +x /usr/local/bin/yq
- pip install outerbounds ob-project-utils pyyaml
- PROJECT_NAME=$(yq .project obproject.toml)
- PLATFORM=$(yq .platform obproject.toml)
- CICD_USER="${PROJECT_NAME//_/-}-cicd"
- |
outerbounds service-principal-configure \
--name $CICD_USER \
--deployment-domain $PLATFORM \
--perimeter default \
--jwt-token $OUTERBOUNDS_ID_TOKEN
- obproject-deploy
artifacts:
paths:
- deployment_summary.md
when: always
Using Outerbounds with Azure DevOps
Azure DevOps supports OIDC through Azure AD federation.
Example azure-pipelines.yml
trigger:
- main
pr:
- main
pool:
vmImage: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- checkout: self
- task: AzureCLI@2
displayName: 'Configure Outerbounds'
inputs:
azureSubscription: 'your-azure-connection' # Replace with your service connection
addSpnToEnvironment: true
scriptType: bash
scriptLocation: inlineScript
inlineScript: |
wget -qO /usr/local/bin/yq https://github.com/mikefarah/yq/releases/latest/download/yq_linux_amd64
chmod +x /usr/local/bin/yq
PROJECT_NAME=$(yq .project obproject.toml)
PLATFORM=$(yq .platform obproject.toml)
CICD_USER="${PROJECT_NAME//_/-}-cicd"
pip install outerbounds ob-project-utils pyyaml
outerbounds service-principal-configure \
--name $CICD_USER \
--deployment-domain $PLATFORM \
--perimeter default \
--jwt-token $idToken
- script: obproject-deploy
displayName: 'Deploy Project'
env:
SYSTEM_ACCESSTOKEN: $(System.AccessToken)
Using Outerbounds with CircleCI
CircleCI supports OIDC tokens for secure authentication.
Example .circleci/config.yml
version: 2.1
jobs:
deploy:
docker:
- image: cimg/python:3.12
steps:
- checkout
- run:
name: Install dependencies
command: |
wget -qO /usr/local/bin/yq https://github.com/mikefarah/yq/releases/latest/download/yq_linux_amd64
chmod +x /usr/local/bin/yq
pip install outerbounds ob-project-utils pyyaml
- run:
name: Configure Outerbounds
command: |
PROJECT_NAME=$(yq .project obproject.toml)
PLATFORM=$(yq .platform obproject.toml)
CICD_USER="${PROJECT_NAME//_/-}-cicd"
outerbounds service-principal-configure \
--name $CICD_USER \
--deployment-domain $PLATFORM \
--perimeter default \
--jwt-token $CIRCLE_OIDC_TOKEN_V2
- run:
name: Deploy Project
command: obproject-deploy
workflows:
deploy:
jobs:
- deploy:
context: [OIDC_CONTEXT] # CircleCI context with OIDC enabled
filters:
branches:
only: [main]
Don't hesitate to contact support on Slack if you need help setting up GitOps effectively in your environment.